When you’re working with HTML tables, borders are one of the quickest ways to make your data easier to read and visually organized.
While the basic border attribute works for simple tables, CSS offers far more control over how borders appear, including style, thickness, color, spacing, and advanced effects like rounded corners and shadows.
This guide explains how to create and style table borders step by step. You’ll see practical examples for basic HTML tables, learn how to apply CSS for precise customization, and discover solutions for common display issues.
Table of Contents
Basic HTML Table Structure
Before you can style table borders, it’s important to understand how an HTML table is structured. At its core, a table is built from just a few essential tags:
Basic HTML Table Tags (<table>, <tr>, <td>, <th>)
<table>: The grand container of all table elements.<tr>(table row): Within the table, there’s the<tr>tag. This tag is like the backbone, supporting each row.<td>(table data): Nested in each row, the<td>tags hold the individual data cells.<th>(table header): When a row needs a header, in comes the<th>tag – bold and centered, showing off its importance.
Example of a Simple HTML Table
This simple table provides a foundation to which you can later add borders, spacing, and styling with CSS. Understanding these basic elements ensures that any customization will remain structured and accessible.
<table>
<tr>
<th>Header 1</th>
<th>Header 2</th>
<th>Header 3</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Data 1</td>
<td>Data 2</td>
<td>Data 3</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Data 4</td>
<td>Data 5</td>
<td>Data 6</td>
</tr>
</table>How to Add Borders to HTML Tables? Step-by-Step
There are two main ways to add borders to HTML tables: using the HTML border attribute or applying CSS. While the HTML attribute is simple, CSS offers far more flexibility and control.
#1 Way: Using the HTML Border Attribute
The border attribute is the simplest way to add borders directly in HTML. It’s easy to implement but limited in customization.
Syntax and Implementation
Here’s the syntax, plain and straightforward:
<table border="1">
<!-- rows and cells go here -->
</table>
In the blink of an eye, borders appear. A straightforward approach — like grabbing the first pencil you see.
Example with HTML Border Attribute
This method quickly adds visible borders to each table cell. However, it doesn’t allow advanced styling such as color, thickness, or spacing adjustments. For more control, CSS is recommended.
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>Item</th>
<th>Quantity</th>
<th>Price</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Apples</td>
<td>10</td>
<td>$1.00</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Oranges</td>
<td>5</td>
<td>$2.00</td>
</tr>
</table>
#2 Way: Using CSS for Table Borders
CSS provides full control over table borders, allowing you to adjust style, width, color, and spacing. Using CSS is the preferred approach for modern web design.
Example with CSS Border Property
With CSS, you can also apply different border styles (dashed, dotted, double), set unique colors, adjust thickness, and control spacing with properties like border-collapse and border-spacing.
<style>
table, th, td {
border: 1px solid black;
}
</style>
<table>
<tr>
<th>Item</th>
<th>Quantity</th>
<th>Price</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Bananas</td>
<td>6</td>
<td>$1.20</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Grapes</td>
<td>2</td>
<td>$3.50</td>
</tr>
</table>How to Style and Customize Table Borders
Customizing table borders with CSS allows you to control the appearance of your tables and make them more visually structured. This section covers essential techniques for border behavior, styling, and finishing touches.
Make Table Borders Collapse
The border-collapse property determines how the borders between cells are rendered. By default, tables use separate, which keeps each cell’s border distinct.
Using collapse merges adjacent borders into a single line, creating a cleaner, more unified appearance.
- When to use
collapse: Best for tables where a sleek, grid-like look is desired, such as data tables, schedules, or pricing tables. - When to use
separate: Ideal if you want spacing between cells or need rounded corners on individual cells.
Collapsing borders can also reduce visual clutter in tables with many rows and columns, making data easier to read.
Example of Collapsed Table Borders
Imagine a table that whispers sophistication through its neatly unified borders:
<style>
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
}
th, td {
border: 1px solid black;
}
</style>
<table>
<tr>
<th>Weekday</th>
<th>Task</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Monday</td>
<td>Meeting</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Tuesday</td>
<td>Workshop</td>
</tr>
</table>
Customizing Border Width
The border-width property allows you to control how thick or thin your table lines appear. This can affect both readability and style:
- Thin borders (1-2px): Minimalist, subtle, and professional.
- Medium borders (3-4px): Draw attention to important tables or separate sections.
- Thick borders (5px+): Strong visual emphasis, useful for highlighting summary rows or headers.
Choosing the right thickness depends on the table’s purpose and the overall page design.
Change Border Color
The border-color property lets you move beyond standard black borders. Color can be used to:
- Match your website’s theme or branding
- Highlight certain rows, columns, or headers
- Differentiate sections within the same table
For instance, a pricing table might use bold colors for headers, while a data table could use subtle shades to separate sections without distracting the reader.
Apply Different Border Styles
CSS provides a wide range of border styles that let you control the visual texture of your table:
- Solid: A continuous line; simple and clean.
- Dotted: Small dots; great for subtle separation.
- Dashed: Short dashes; modern and casual.
- Double: Two parallel lines; good for emphasizing headers or totals.
- Groove/Ridge/Inset/Outset: 3D-like effects; adds depth for stylized tables.
- None/Hidden: Remove borders entirely when spacing or minimalism is preferred.
Using a mix of styles can create a hierarchy of information – for example, solid borders for headers and dotted lines for data cells.
Example of Various Border Styles
Visions danced through my mind when seeing all these styles in action:
<style>
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
}
th, td {
border-width: 2px;
border-color: green;
border-style: solid;
}
th {
border-style: double;
}
td.dotted {
border-style: dotted;
}
td.dashed {
border-style: dashed;
}
</style>
<table>
<tr>
<th>Type</th>
<th>Example</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td class="dotted">Dotted</td>
<td class="dotted">Dotted border</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td class="dashed">Dashed</td>
<td class="dashed">Dashed border</td>
</tr>
</table>
A table wearing multiple outfits, each cell showcasing a new style.
Adding Rounded Borders
The border-radius property softens table corners, giving a modern, approachable look. Rounded borders are particularly effective in tables used in dashboards, forms, or interactive interfaces.
Tips for rounded borders:
- Use
border-collapse: separateto prevent corners from being clipped. - Adjust radius proportionally to the size of table cells.
- Combine with subtle border colors for a sleek, polished look.
Rounded borders help tables appear less rigid and can improve the visual flow of a page, especially when paired with other rounded UI elements.
Table with Rounded Borders
<style>
table {
border-collapse: separate;
}
th, td {
border: 2px solid purple;
border-radius: 15px;
}
</style>
<table>
<tr>
<th>Event</th>
<th>Date</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Conference</td>
<td>March 10</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Workshop</td>
<td>April 22</td>
</tr>
</table>
Additional Tips for Table Border Customization
- Combine multiple properties: Adjust width, color, and style together to create a cohesive look.
- Use classes for reusable styles: Instead of inline CSS, define classes for different table types to maintain consistency across pages.
- Consider accessibility: Make sure border contrasts are sufficient for readability, especially for visually impaired users.
- Test across browsers: CSS rendering may differ slightly between browsers, so verify your tables look consistent everywhere.
Why Use wpDataTables to Build and Customize Tables – Without Coding
If you want powerful, interactive tables on your WordPress site without diving into HTML or CSS, wpDataTables is a top-tier solution. It’s built specifically for users who need to create, manage, and style complex data tables – all from a friendly interface.
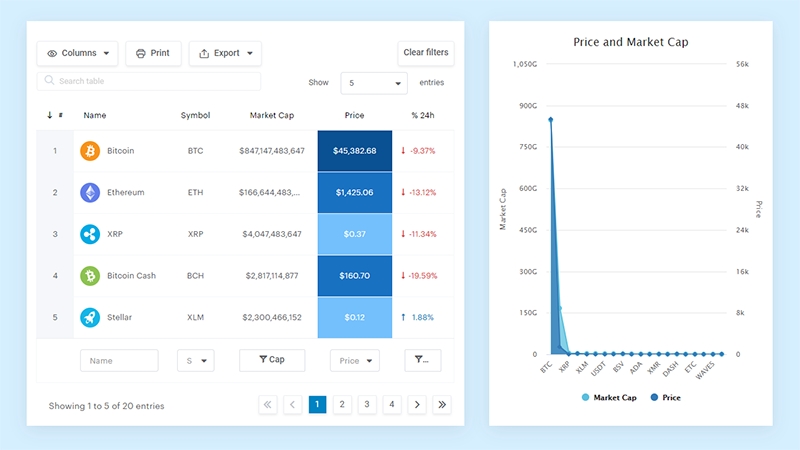
No Coding Required for Table Creation
With the Table Creation Wizard, you can build a table from scratch – define rows, columns, and structure – directly in your WP admin. You don’t need to know SQL, HTML, or anything technical.
Import Data from Any Source
Bring in data from Excel, CSV, Google Sheets, JSON, XML, or a MySQL database – without writing a single line of code.
Customize Table Appearance Visually
Use the “Customize” settings panel in the wpDataTables dashboard to control everything:
- Fonts (size, color).
- Header styles (background color, text color, hover effect).
- Borders (inner cell borders, outer table borders, or even removing them).
- Row colors (alternate row backgrounds, hover color).
- Table pagination style and colors.
- Custom CSS (if you want to add your own tweaks).
Responsive Design Out-of-the-Box
Tables created with wpDataTables can adapt for mobile, tablet, and desktop – no extra CSS needed.
Advanced Features Without Complexity
Get features like sorting, filtering, conditional formatting, and calculated columns.
Bottom line: With wpDataTables, you don’t need to be a developer to build sophisticated, data-rich tables. Whether you’re working with large datasets, background imports, or need full control over styling – wpDataTables gives you a powerful, intuitive way to deliver professional tables on your WordPress site.
It’s as simple as:
- You provide the table data
- Configure and customize it
- Publish it in a post or page
And it’s not just pretty, but also practical. You can make large tables with up to millions of rows, or you can use advanced filters and search, or you can go wild and make it editable.
“Yeah, but I just like Excel too much and there’s nothing like that on websites”. Yeah, there is. You can use conditional formatting like in Excel or Google Sheets.
Did I tell you you can create charts too with your data? And that’s only a small part. There are lots of other features for you.
Check out the pricing and choose plan that suits your table-building needs!
How to Apply CSS to Customize Table Borders?
CSS gives you complete control over table borders, allowing for precise styling, better maintainability, and consistent design across your site.
There are multiple ways to apply CSS: inline, internal, or external. Each method has its own use cases, advantages, and drawbacks.
Inline CSS
Inline CSS is applied directly to HTML elements using the style attribute. It’s fast and convenient for small changes or quick testing, but it doesn’t scale well for larger projects.
Key Points:
- Ideal for one-off tables or rapid prototyping.
- Overrides other CSS rules if conflicting styles exist.
- Not recommended for large websites because it mixes structure and style.
Inline CSS is useful when you need immediate results or want to demonstrate a style without creating additional files. However, for consistency and maintainability, other CSS methods are preferred for production sites.
Example of Inline CSS for Table Borders
Consider this:
<table style="border: 3px dashed black; width: 80%;">
<tr>
<th style="border: 1px solid black; padding: 10px;">Name</th>
<th style="border: 1px solid black; padding: 10px;">Role</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td style="border: 1px solid grey; padding: 10px;">Alice</td>
<td style="border: 1px solid grey; padding: 10px;">Developer</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td style="border: 1px solid grey; padding: 10px;">Bob</td>
<td style="border: 1px solid grey; padding: 10px;">Designer</td>
</tr>
</table>
Color-coded borders for each cell, like jazz riffs painted on a visual canvas.
External CSS
External CSS involves writing all styles in a separate .css file and linking it to your HTML. This method is scalable, maintainable, and aligns with modern web development best practices.
Benefits of External CSS:
- Scalability: Easily style multiple tables across your website from one file.
- Maintainability: Update styles in one place and changes automatically reflect everywhere.
- Separation of Concerns: Keeps HTML structure clean and focuses purely on content while CSS handles the presentation.
Using external CSS allows you to define border width, style, color, padding, and spacing consistently. You can also create reusable classes for different table designs, ensuring uniformity across your website.
Example with External CSS
Let’s say you’ve got a styles.css file. Inside, it’s a treasure trove of wonders.
/* styles.css */
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
width: 100%;
}
th, td {
border: 2px solid purple;
padding: 15px;
}
th {
background-color: #f2f2f2;
}
And your HTML? A minimalist whisper, leaning on its robust partner.
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css">
</head>
<body>
<table>
<tr>
<th>Planet</th>
<th>Diameter</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Earth</td>
<td>12,742 km</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Mars</td>
<td>6,779 km</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>Choosing the Right Approach
- Inline CSS: Quick, temporary, or for demos.
- Internal CSS (inside
<style>tags): Useful for single-page projects. - External CSS: Best for larger projects, reusable table styles, and long-term maintainability.
You can choose the right approach for your project and apply table borders efficiently without duplicating code or compromising design consistency.
Advanced Table Border Customization Techniques
Once you’re comfortable with basic borders, CSS allows for more advanced techniques that give your tables a distinct, polished look. By combining different styles, colors, and thicknesses, you can highlight hierarchy, improve readability, and create visually engaging tables.
Combining Multiple Styles
Borders don’t have to be uniform. Each side of a cell – top, right, bottom, and left—can have a unique style, thickness, and color. This approach can help emphasize different aspects of a table or create a visually dynamic layout.
- Top border: Solid, thick line for emphasis
- Right border: Dashed or dotted to differentiate sections
- Bottom border: Double line for separation
- Left border: Groove or ridge for depth
Example of Combined Border Styles
By combining styles, you can give your tables a layered, textured appearance while maintaining clarity. This is particularly useful for dashboards, reports, or tables with multiple categories.
<style>
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
}
th, td {
border-top: 2px solid black;
border-right: 2px dashed blue;
border-bottom: 2px double green;
border-left: 2px groove purple;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
<table>
<tr>
<th>Art Form</th>
<th>Complexity</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Painting</td>
<td>Advanced</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Sculpture</td>
<td>Medium</td>
</tr>
</table>Customizing Borders for Specific Elements
Customizing borders differently for headers and data cells allows you to create a hierarchy of information and guide readers’ attention effectively.
Table Header (<th>) Borders
- Strong, bold borders to define headers
- Optional background color to make headers stand out
- Uppercase or other typographic styling for emphasis
Table Data (<td>) Borders
- Lighter or dotted borders for data cells to contrast with headers
- Consistent padding for readability
- Optional color coding for categories or status indicators
Layered Visual Effects
Advanced techniques can include:
- Color gradients or alternating border colors to visually separate rows or columns.
- Mixed border widths to emphasize certain rows, columns, or key data points.
- Subtle 3D effects like
groove,ridge, orinsetto give depth without cluttering the table.
These techniques are particularly useful for complex tables, like schedules, comparison charts, or product inventories, where visual hierarchy is key.
Example of Customized Borders for Specific Elements
An example where headers and data cells stand in harmony yet distinct, each with their own flair.
<style>
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
width: 100%;
}
th {
border: 3px solid darkred;
background-color: #f0f0f0;
text-transform: uppercase;
padding: 12px;
}
td {
border: 1px dotted darkgreen;
padding: 8px;
}
</style>
<table>
<tr>
<th>Component</th>
<th>Status</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Engine</td>
<td>Operational</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Wheels</td>
<td>In Use</td>
</tr>
</table>FAQ On Stylizing A Table Border In HTML
How can I add a simple border to an HTML table?
Just need to set the border attribute directly in your table tag. Simple:
<table border="1">
<!-- rows and cells here -->
</table>
There you go! A straightforward way to get that basic border around your table.
How do I use CSS to style table borders?
CSS does the heavy lifting. Use the border property in your styles:
table, th, td {
border: 1px solid black;
}
This way, you achieve consistent styling for the entire table, including table data and table headers.
What is the border-collapse CSS property, and why use it?
border-collapse merges the borders between table cells. This unifies your borders.
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
}
It cleans up the design, creating a seamless grid without double borders.
How can I change the border color of my table?
Setting the border color is simple with CSS. Just add:
th, td {
border: 1px solid blue;
}
This gives each cell a nice, blue border. Tweak the color to fit your design.
How do I create different border styles?
CSS allows for various styles like solid, dashed, dotted:
th, td {
border-style: dotted;
}
Try out different styles for a unique look for each table element.
Can I make the table borders rounded?
Yes! Use the border-radius property for adding smooth, rounded edges.
th, td {
border-radius: 10px;
}
This softens your table, making it visually more pleasing.
How do I apply different border styles to specific table elements?
Style table headers and table data separately:
th {
border: 2px solid red;
}
td {
border: 1px dotted blue;
}
This gives your table a customized touch, highlighting important sections.
What’s the syntax for inline CSS for table borders?
Inline CSS places styles directly within the HTML tags:
<td style="border: 1px solid black;">Data</td>
Quick and effective for small adjustments, but not scalable.
How do I use external CSS to style table borders?
Link an external CSS file in your HTML:
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css">
</head>
Then, define your styles in styles.css for a more maintainable approach.
How can I use multiple border styles in one table?
Mix and match different borders using CSS properties.
th, td {
border-top: 2px solid black;
border-right: 2px dashed blue;
border-bottom: 2px double green;
border-left: 2px groove purple;
}
This creates a visually dynamic table with varying border styles.
Conclusion
Mastering how to stylize a table border in HTML unveils a world of creative possibilities. By leveraging HTML and CSS together, we transform mundane tables into data-rich visuals that captivate and guide users.
Whether you’re employing the straightforward border attribute for quick fixes or diving into the deep complexity of CSS properties like border-collapse, border-radius, and intricate border styles – each method brings its charm.
Let’s not forget the flexibility of Inline CSS for one-off adjustments versus the scalability of External CSS for large projects. Each technique has its nuance and application, making your webpage not just functional but beautifully structured.