Ever wondered how the backbone of your favorite WordPress site functions when it comes to managing content? Understanding where WordPress pages are stored unveils a crucial aspect of optimizing and securing your website.
In this article, dive deep into the anatomy of WordPress storage— a key to enhancing site performance, securing data, and optimizing your Content Management System (CMS).
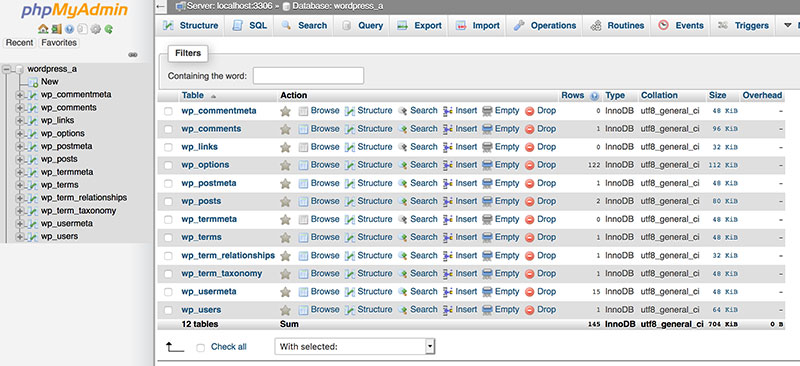
By exploring the WordPress Database and its robust structure, you’ll gain insights into how pages, posts, and settings reside within specialized Data Tables. This guide will map out how MySQL, coupled with wp-config configurations and WP Database Tables like wp_posts, orchestrates your data seamlessly.
Prepare to navigate through web hosting environments, understand File System layouts, and handle file management effectively.
This exploration will equip you with the strategic know-how to manage your WordPress data with precision, ensuring operational excellence and security-centric practices.
Table of Contents
Where are WordPress Pages Stored?
WordPress pages are stored in the MySQL database associated with your WordPress site. Specifically, the content of the pages is found in the wp_posts table, where each page is a record with a post_type of ‘page’. This includes the page’s content, title, and other metadata.
How Does WordPress Database Work?
Before you know the answer to where WordPress pages are stored, you need to learn about the WordPress basics. That includes the WordPress database and how it processes.
When you use WordPress as a content management system, it creates a static HTML file for your site’s pages. The database takes over the storage of all your pages’ content. Every time the page is loading, WordPress uses codes to gain access.
Some people might say, “My website works fine even without knowing how it works!”. However, knowing how the WordPress database stores and processes your information has many advantages. One of these is that you will learn how to resolve WordPress issues on your own.
Each WordPress page contains theme files, such as single.php for blog posts and page.php. Sometimes, the template defines and arranges additional custom posts for your content. On the other hand, the database (MySQL DB) stores information, images, text, embeds, and more. That means you need to search through the MYSQL database to access your website content.
Apart from the database, WordPress comes with two more elements:
- Any plugins, themes, files, or media attachments you upload to your site
- The core files you install to run WordPress itself
You can write code to create your website’s pages. However, that will take time and resources to create one. Instead, you can use the WordPress element to build pages on your site.
Once you visit a website, that will signal the database to present the required content by loading a set of PHP scripts. Then, it processes and builds an HTML page on the fly. Finally, that will send the page to your browser.
Through the process of a database, you are putting the dynamic content altogether into a cohesive page. WordPress gathers the dynamic content from various sources, such as the page content, header, sidebar, and footer.
How to Generate the HTML Pages for Your Visitors
- The user selects a particular page from your WordPress website.
- The PHP function, which starts with index.php, starts to load.
- It will signal the database about the particular page you select.
- WordPress will generate an HTML page by compiling the data, together with the plugins and themes.
- The database will render the requested HTML page.
This step is possible through MySQL, which generates HTML pages for your page’s visitors. That also means you don’t need to keep each page for every post on your server.
Where are WordPress Pages Stored
Take note that the WordPress database stores specific items and pages from your website. This includes the following:
- User’s data and settings
- Your website’s general settings (plugins, themes, site’s title, and description
- Your site’s attachment information (file name, alt text, description, and pages or posts information)
- Your site’s metadata, which includes the post categories, tags, custom taxonomies, custom field, and plugins’ metadata
- Custom post types, posts, and pages
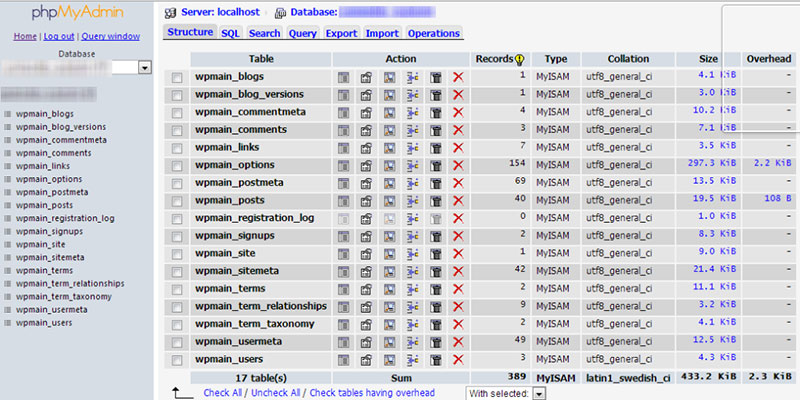
WordPress database stores your pages and posts by dividing all the items into 12 tables. All tables connect one another, and they are all essential in keeping your pages and posts in a safe place. Out of all the database tables, wp_posts is the most important one.
Here are the WordPress database tables and their purposes:
- wp_usermeta: saves metadata on your users
- wp_users: saves the user’s data on your site, including their password and username
- wp_termmeta: saves metadata on your taxonomy terms
- wp_term_relationships: stores the posts assignment to categories, saving the post and other types of contributions, also known as “terms.”
- wp_term_taxonomy: saves the taxonomy of wp_terms table’s term
- wp_terms: saves all your site’s taxonomy terms, such as the tags and categories
- wp_commentmeta: saves all the metadata of your site’s comments
- wp_comments: saves all your posts’ comments, which includes the time and the poster’s name
- wp_postmeta: stores all the metadata from the wp_posts, like the custom fields and editing lock
- wp_posts: stores every file or content of your website, including the title, text content, modification date, creation date, author, and the publishing status excerpt.
Each one of these is essential for keeping your WordPress pages organized. Having these tables can help you to know where all your posts and pages are stored.
The Instructions on How to Access WordPress Pages Through phpMyAdmin
So far, you have learned where WordPress pages are stored in the MySQL database. Apart from that, you need to know how to access the files and tables in the SQL DB.
Take note: Mostly, it is useless to edit your page/post data outside the WordPress dashboard. If needed, you can only attempt to edit the database if you know exactly how to do it, because you could delete important files from your database.
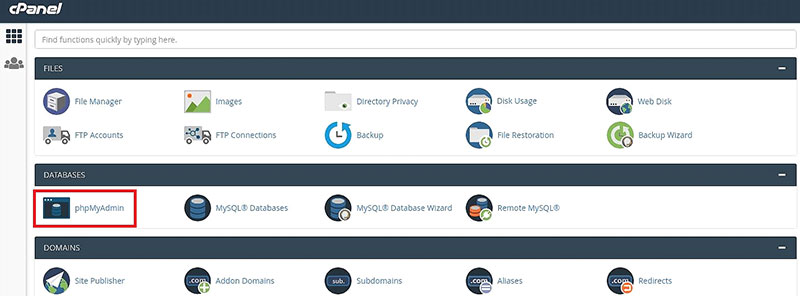
Here are the steps to access your pages:
- Use the phpMyAdmin tool by logging in to your cPanel account, then select the PHPMyAdmin icon.
- Pick the name for your WordPress installation’s database name
- Select the wp_posts sub-table
- Click the corresponding “Browse,” then the stored content posts, pages, and custom posts appear.
- Search for the post_type field to find pages or posts according to their categories
All the entries you have included to your post_type pages are the real page content of your website. If you want to edit them, select the “Edit” link for a code or direct content via PHPMyAdmin.
The Ultimate Guide on How to Manually Backup Your WordPress Site Databases
Every WordPress website comes with an open-source nature. That is why your website can be vulnerable to hackers by tracking the security and scrutinizing the underlying code.
Apart from the potential risk of being hacked, the unexpected might happen. One of these could be sudden crash downs or the accidental loss of your web page data.
Sometimes, even though you purchase the most expensive or high-rated security plugin, it cannot help save your files. Having a backup is crucial to keep your data.
You need to have various code copies to restore the website when problems occur. As a result, you will keep your potential customers in the long run.
Here is the ultimate guide to backup your database via phpMyAdmin:
- Login to your cPanel of your server, then select phpMyAdmin.
- The database page will appear and present all your databases.
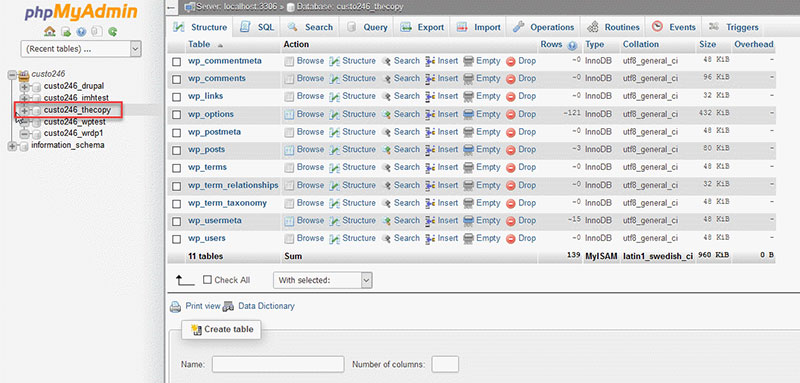
- Select the database you want to backup.
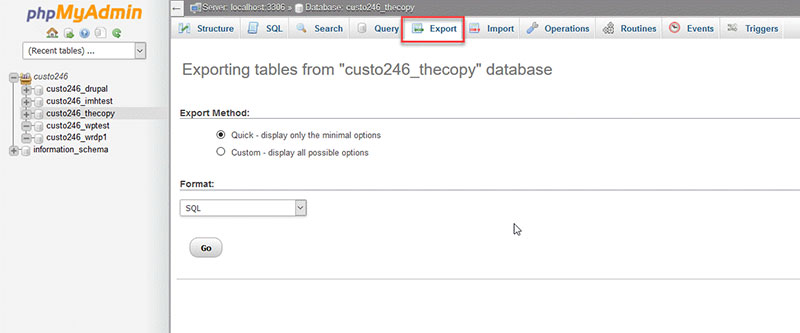
- Choose the “Export” option when you are inside the database.
- It will redirect to the export page.
- Then, download the WordPress server backup.
- It will show the two ways of exporting and formatting your database—Quick and Custom. Select the method according to your preference.
- Select the SQL file format to store your SQL database.
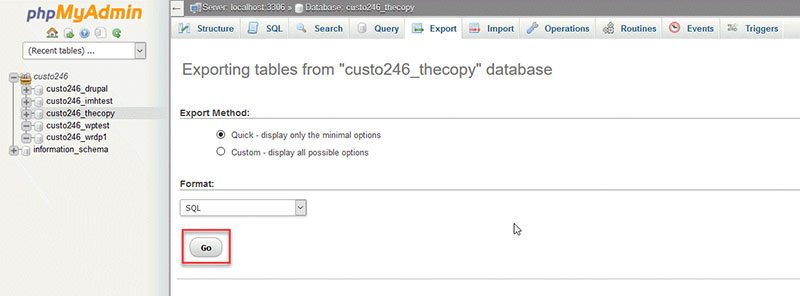
- Click “Go,” and the database downloading begins
FAQs about where the WordPress pages are stored
How do I access the WordPress database?
Access the WordPress database through tools like phpMyAdmin, typically offered by your web hosting service. Here, you can view and manage your WordPress data, including wp-content, which contains themes and plugins, enabling site personalization and efficiency enhancements.
What is the wp-config file?
The wp-config.php file is a crucial WordPress file that houses important configuration information, such as database connection settings and Security Keys. It’s the roadmap for how WordPress communicates with its database, ensuring smooth data operations and SSL Encryption.
How do pages connect to other data in WordPress?
Pages in WordPress are linked to various types of metadata and comments stored in other tables like wp_postmeta and wp_comments. These connections help organize and retrieve page-related data efficiently, impacting the overall performance optimization of your WordPress site.
Can I store WordPress pages on a different server?
Technically, you can store the WordPress database and site files on different servers, but setup involves web server configuration and adjustments in wp-config for directing WordPress to the external database, emphasizing the importance of robust server-side storage management.
What happens to my pages if I change my WordPress database?
Changing your WordPress database, such as migrating to a new server or changing database prefixes, requires careful updates in the wp-config file and consistent data backup practices. Ensure all URLs and internal paths in the new database reflect the current data arrangement to avoid data loss.
How do WordPress pages utilize caching?
WordPress caching mechanisms enhance your site’s load times by storing static versions of your content in temporary storage. This approach minimizes database calls for your WordPress pages, which is particularly noticeable with data retrieval in high-traffic situations.
Is it secure to store sensitive pages in WordPress?
Security for stored pages in WordPress can be fortified using SSL Encryption and robust Data Backup solutions. Implementing security plugins and routine database checks helps protect against unauthorized access and data breaches, ensuring securely storing WordPress data is a priority.
How can I optimize the storage of my WordPress pages?
Optimizing storage involves regular database optimization WordPress practices, such as cleaning up stale meta-data and optimizing SQL tables. Using tools to review and refine the structure and indices of your database can lead to significant improvements in how quickly and efficiently your pages load.
Are there plugins to help manage where WordPress pages are stored?
Yes, several WordPress storage plugins are available that help manage database interactions and file placements. These plugins can automate and streamline backup processes, data cleanup, and even content delivery networks (CDNs) integration, thus enhancing your WordPress File System management.
Conclusion
Diving deep into where WordPress pages are stored reveals much more than just the intricacies of database tables and file directories. It underscores the essence of efficient content management and the importance of a secure, well-organized WordPress Database structure.
- Reflect on how knowledge of database structure aids in troubleshooting and customization.
- Appreciate the role of good hosting and security practices.
Mastering this aspect of WordPress not only enhances your site’s performance but also fortifies it against potential security threats. Embracing Database Optimization and utilizing WordPress Storage Plugins can transform this technical knowledge into practical, actionable strategies that safeguard data and streamline operations.
Harness these insights to wield complete control over your digital space, ensuring that every piece of content is exactly where it should be—secure, accessible, and performing at its best.
If you enjoyed reading this article on where WordPress pages are stored, you should read this one on how to scan the WordPress database for malware.
We also wrote about a few related subjects like the WordPress database schema, WordPress database plugins, doing a WordPress database cleanup, or how to find and replace an URL in a WordPress database.