Unlocking the full potential of your WordPress website hinges on one crucial factor: user roles. Imagine having a finely tuned team where everyone knows their exact responsibilities, ensuring smooth and efficient workflow. That’s the power of mastering WordPress user roles.
In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of WordPress user roles—from Administrator privileges to Subscriber capabilities—and why understanding these roles is pivotal for effective user management and site security.
By the end, you’ll not only grasp the hierarchy and permissions settings but also learn how to leverage these roles to enhance your content management strategy.
Expect to uncover tips on customizing roles with plugins and maintaining strict access control for multi-user setups. Ready to elevate your site’s functionality? Let’s get started on optimizing your WordPress dashboard for seamless role-based access.
Table of Contents
What are WordPress user roles?
WordPress user roles define permissions and access levels for site users. The main roles are Administrator, Editor, Author, Contributor, and Subscriber, each with specific capabilities for site management and content creation.
WordPress roles explained in less than a minute
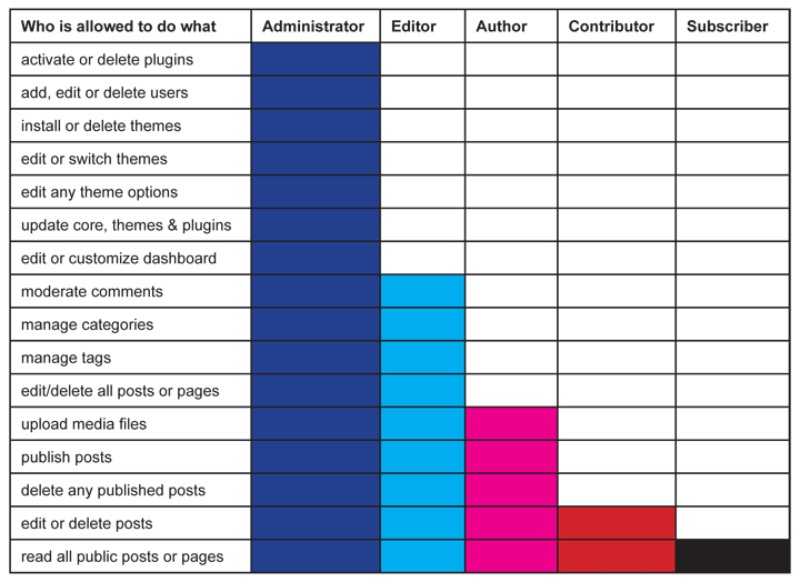
As we already mentioned, WordPress user roles are what defines which user is allowed to do what. To paint a picture, besides other WordPress user permissions, an author can publish a post, while an editor can do that and a bit more – publish pages, for example.
So, different WP roles have different WordPress capabilities. That type of hierarchy helps secure your website and its content and can help you define workflow of your team.
Default WordPress user levels
When you install WordPress, you are given five default user roles. We will list them out below, starting with the one which has the least amount of permissions:
WordPress subscriber role
All new users default to subscriber role. They can read your content, write and post comments, and create a profile using your dashboards – and that is it!
Quick tip: If you want your readers to register on your website without too much hassle, go to settings, general, membership, and check “Anyone can register” box. Then, find the Meta widget in appearance, widgets, and add it to your sidebar.
WordPress contributor role
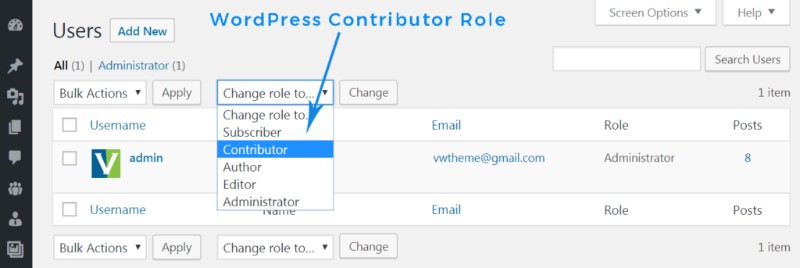
Something more exciting: contributors are allowed to write posts, edit them, and delete their unpublished posts, with a catch. An admin or an editor must review and publish the written post, and they will also have to assist the contributor with images, videos and audio files since they cannot access the media library.
If you think about having a guest blogger, or anyone that does not post regularly, contributor role is for them.
WordPress author role
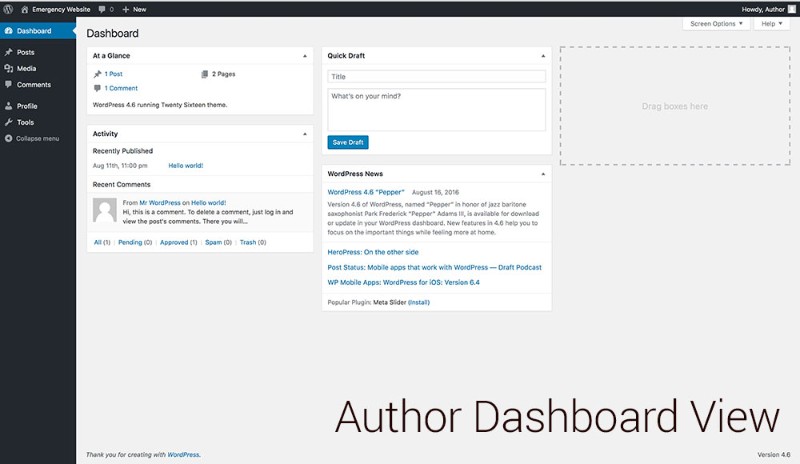
On a first glance, these roles look similar, but if “WordPress contributor vs author” battle would occur, the latter would win.
Authors can write, edit, delete and publish their own posts, as well as upload files into the media library, but they cannot see anything created by other users on the dashboard. Another plus is the ability to moderate comments on their own posts.
Of course, the role has certain limitations: they cannot delete anything from the media library, and can’t create, edit, or delete pages.
WordPress editor role
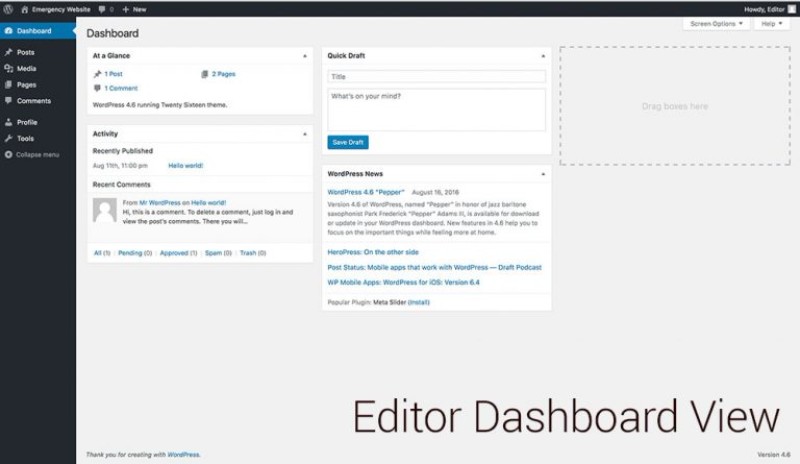
Now we are getting to the interesting part.
In addition to permissions that an author role has, an editor can publish, edit, or delete any page or post, including the private ones. They can moderate comments, manage categories and links.
The role is great for anyone that needs permission to access all of the content, without having the ability to change themes, plugins, widgets, and, most importantly, settings.
WordPress administrator role
An administrator lies at the top of the WordPress permissions hierarchy chain.
He watches over other WordPress users and can perform every action available through the dashboard. Administrators can change themes, modify core files, and change other users’ roles, also have complete control over all content.
Bonus: WordPress super administrator role
This role is not available in standalone WordPress sites, but if your website is a part of WordPress Multisite Network, then you will have a super administrator who is watching over the entire network.
Super administrators can do everything an administrator can – but across the entire multisite network. In addition to that, they can add and delete sites from the network.
Editing Existing User Roles
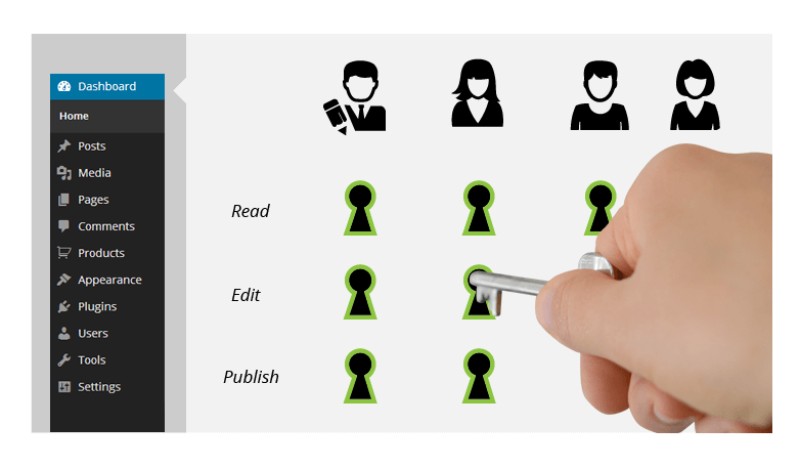

Default WordPress user roles have clearly defined permissions which works for most of the websites, but you can definitely edit those permissions to your liking.
Maybe you think that authors on your website should be able to publish and delete their own posts without having to wait for an editor’s or an admin’s blessing? If you trust your authors, then allowing them to do just that will speed up the workflow.
Of course, the story can be completely different. Having the ability to delete their own posts may spell disaster in case the author leaves the job on bad terms and decides to remove all of his or her posts.
Either way, for the sake of this WordPress user role tutorial, let us assume that you want to remove the permission of authors to delete their own content once published.
The first step is to install and activate WordPress user roles plugin called Capability Manager Enhanced plugin.
Then go to users, capabilities and select the user role you want to change from the top box in the right column, and then click the load button. Uncheck the capabilities that you want to remove from the user, and save changes.
This will load user’s capabilities in the boxes on the left.
How to add WordPress custom user roles?
Using the WordPress user role plugin we just mentioned, you can create custom user roles with their own set of permissions for your website.
Go to user, capabilities and type in the WordPress user role name under “Create New Role”. After that, under “Other WordPress Capabilities” select which permissions you want the custom user to have.
It is simple as that.
How can I effectively apply user roles on my website?
Now that you know how each user role works, it is time to take a look at how to apply them correctly. Here are several tips for making the best out of WordPress user roles which you can use on your website:
- For security reasons, every user should only have the level of access they need.
- Limit the number of top user roles. We suggest having only one administrator and a few trusted editors.
- Assign author role to users which regularly create content for your website, and have earned your trust.
- New and one-time writers and guest bloggers will be more than happy with the contributor role.
- Use a WordPress user roles plugin to customize your user roles. We already talked about Capability Manager Enhanced, but User Role Editor is also a good option.
FAQ on WordPress user roles
How do I assign a user role in WordPress?
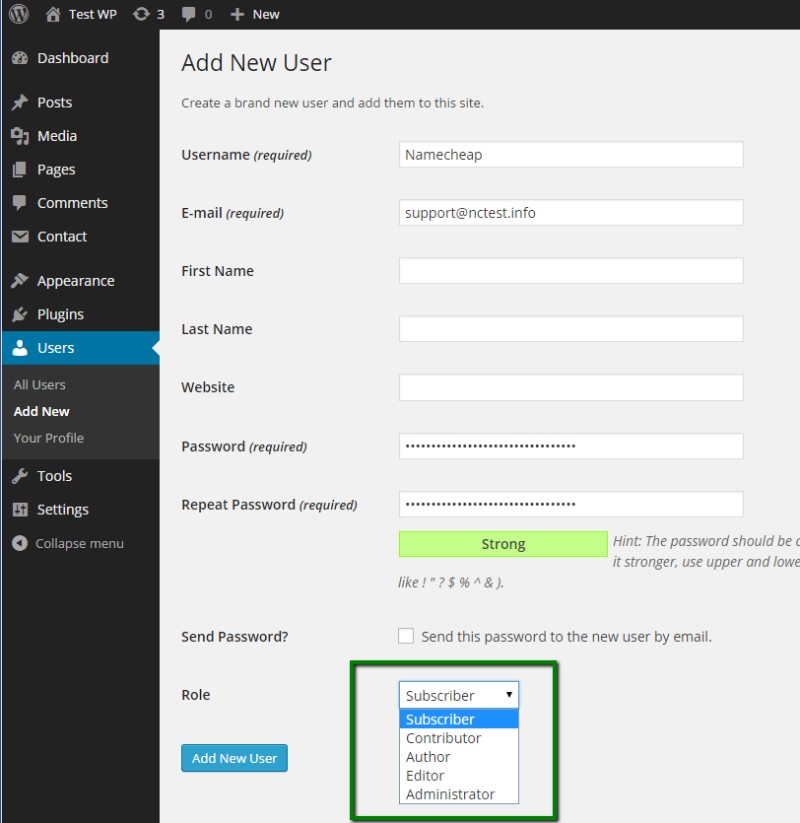
To assign a user role, navigate to the WordPress dashboard, select Users > Add New or edit an existing user. Here, you can choose the desired role from a dropdown menu. This assigns specific permissions settings and capabilities to the user, tailoring their access and functions.
Can I create custom user roles?
Yes, custom user roles can be created using plugins like the User Role Editor. These tools allow you to define unique user roles and capabilities, offering flexibility to match your site’s specific needs and ensuring precise access control for various users.
What is the difference between Administrator and Editor roles?
The Administrator has complete control over the site, including content management, settings, and user roles. The Editor, however, can manage and publish posts, including those by other users, but lacks access to site settings and overall user management functions.
How can I limit user access to specific areas of my WordPress site?
Limiting user access involves configuring role-based access controls. Use plugins like User Role Editor to fine-tune permissions, restricting users to specific areas. This ensures that only authorized users can access sensitive parts of your site, enhancing site security.
What capabilities does the Contributor role have?
Contributors can write and manage their own posts but cannot publish them. They must submit their work for review. This role is ideal for guest authors, as it allows them to create content without granting full editorial or administrative privileges.
How does the Subscriber role function?
Subscribers have the most limited capabilities. They can manage their profiles and leave comments but cannot create or manage posts. This role is typically used for sites requiring user registration for commenting or accessing restricted content, maintaining strict access control.
Can user roles be modified after assignment?
Yes, user roles can be modified anytime. Go to the WordPress dashboard, select Users, and edit the specific user. Here, you can change their role, adjusting their permissions settings to better suit evolving responsibilities or security requirements.
What are the best plugins for managing WordPress user roles?
Top plugins for managing WordPress user roles include User Role Editor, Members, and Capability Manager Enhanced. These tools offer robust features for customizing roles, setting specific capabilities, and ensuring comprehensive role-based access and user management.
Why is understanding WordPress user roles important for site management?
Understanding WordPress user roles is crucial for maintaining a secure, organized, and efficient site. Properly assigned roles and permissions settings streamline content management, enhance site security, and ensure that users have appropriate access levels, preventing unauthorized actions and maintaining workflow integrity.
Conclusion
Mastering WordPress user roles is pivotal for maintaining a well-structured and secure site. By comprehending the intricacies of each role—from Administrator to Subscriber—you ensure that every user operates within defined boundaries, safeguarding your site’s integrity and efficiency.
To recap, understanding user roles isn’t just about knowing what each role can do. It’s about leveraging these roles for effective content management, precise access control, and enhancing user engagement. Utilizing tools like User Role Editor and implementing strategic permissions settings empowers you to tailor roles to your specific needs, ensuring a seamless and secure workflow.
With these insights, you’re equipped to optimize your WordPress site’s functionality and security. Assign roles thoughtfully, customize as needed, and maintain vigilance over user activities. This approach not only boosts productivity but also fortifies your site against unauthorized access and potential security breaches. In the dynamic world of WordPress, mastering user roles is your key to a robust and efficient website.
If you need help with your website, WP Buffs is a 24/7 WordPress website maintenance services for serious website owners & white-label partners. Whether you’re looking after 1 site or 1000, they’ve got your back!
Hopefully, this guide helped you gain a better understanding of WordPress user roles!
If you enjoyed reading this article on how to edit WordPress user roles, you should check out this one about how to reset WordPress.
We also wrote about a few related subjects like how to duplicate a page in WordPress, how to edit HTML in WordPress, how to embed video in WordPress, how to change WordPress URL, how to add JavaScript to WordPress and how to add WordPress featured image.