Ever stopped to think about where it all comes from? Enter the showdown: primary data vs secondary data. Think of it as the difference between taking a fresh photo or using one you found online.
Now, I’ve seen many folks scratch their heads, wondering which one’s more legit or how they even differ.
That’s the itch this piece aims to scratch.
By the end of our little exploration, you’ll be able to sift through data like a pro, understanding where it hails from and its quality. We’re talking origins, advantages, pitfalls, and when to use which.
Table of Contents
Primary Data: A Closer Look
Definition and Characteristics
The allure of primary data isn’t shrouded in mystery, it’s about embracing the purity and authenticity of data right from the source.
In the realm of research, especially, primary data is akin to the bread and butter of the investigation. This kind of data is plucked straight from the source, unscathed by previous analyses or interpretations.
The thing about primary data, it’s genuine and unfiltered, offering a sincere glance into whatever it is we’re studying. It’s the first-hand account of an event, it’s the original lyrics scribbled on a napkin by the songwriter, and it’s the direct observations that a scientist jots down during their experiment.
Sources of Primary Data
When it comes to gathering this raw information, where does one even start? There’s a universe of methods to explore when embarking on this data collection journey.
- Interviews are like those heart-to-heart talks where each response is a golden nugget of info.
- Surveys and questionnaires? Think of them as mass text messages, sending out a bunch of questions into the universe and eagerly awaiting the ping of replies.
- Field observations – It’s about being the unseen observer, watching and noting down the phenomena as they unfold.
- Experiments, it’s where curiosity and hypotheses dance in a controlled setup.
There’s more, right? Like the stories encapsulated within life histories and the deeply contextual insights buried in ethnographic research. All of these, they’re pathways leading toward the treasure trove of primary data, each method offering a different lens through which to view the information.
Advantages of Primary Data
Primary data vs secondary data? When opting for the former, we are prioritizing accuracy, a bespoke fit for our research needs, and oftentimes, a fresher, more current snapshot of the situation or context.
Imagine having your very own personal chef, preparing meals tailor-made to your preferences. That’s akin to the exclusivity and specificity primary data can bring to your research table.
Yes, being the sole owner of the data is sort of like having a secret recipe; it ensures a level of exclusivity and control over the information which is particularly crucial in competitive research fields.
Disadvantages of Primary Data
Opting for primary data isn’t always a bed of roses. It’s like opting for a handcrafted, artisanal product – it demands time, resources, and a lot of patience. Crafting a questionnaire or conducting interviews, these can be labor-intensive and quite the coin-drainers.
And ah, the potential pitfalls of biases! They can sneakily embed themselves into data collection, coloring the data in shades that might deviate from the true palette of information.
Navigating through the primary data collection can sometimes feel like wandering through a lush forest with a compass; the path might not always be straightforward, and unexpected challenges (like limitations related to sample size, or logistical hurdles) can pop up, demanding creative solutions on the fly.
Your beautiful data deserves to be online
wpDataTables can make it that way. There’s a good reason why it’s the #1 WordPress plugin for creating responsive tables and charts.
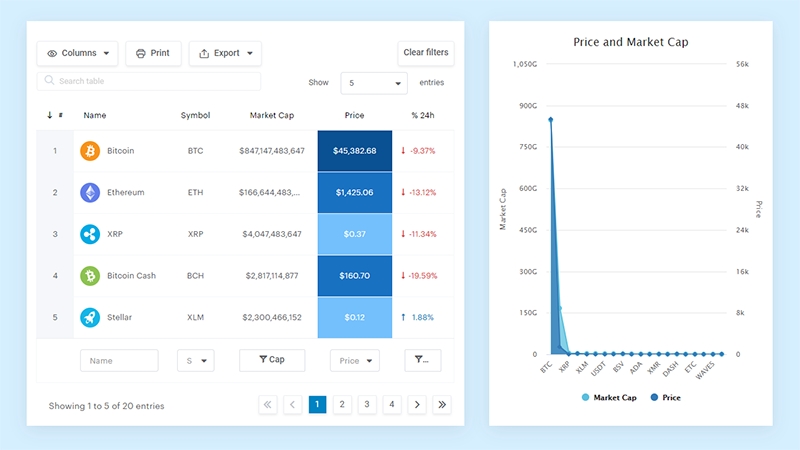
And it’s really easy to do something like this:
- You provide the table data
- Configure and customize it
- Publish it in a post or page
And it’s not just pretty, but also practical. You can make large tables with up to millions of rows, or you can use advanced filters and search, or you can go wild and make it editable.
“Yeah, but I just like Excel too much and there’s nothing like that on websites”. Yeah, there is. You can use conditional formatting like in Excel or Google Sheets.
Did I tell you you can create charts too with your data? And that’s only a small part. There are lots of other features for you.
Secondary Data: Diving into Existing Information
Definition and Characteristics
Alright, so we’ve been vibing with primary data, that fresh-from-the-source, just-squeezed orange juice type of info.
But now, let’s slide over to the flip side of the coin: secondary data. Imagine a pre-packaged smoothie blend, using that fresh juice and mixing it up with other flavors.
That’s kinda like secondary data in the grand scheme of primary data vs secondary data.
Secondary data is all about making the most of what’s already out there. You see, it’s not fresh off the boat; it’s been around the block.
It’s data that was initially collected for some other purpose, maybe another study, maybe a news report, or even just some internal records.
Sources of Secondary Data
Picture yourself on a digital scavenger hunt. Where do you reckon you’d find this data treasure?
- Previous research studies and reports? Oh, totally. These are the archives, the libraries of old. Every piece of research ever done? A potential goldmine.
- Mass media products? Absolutely. Every article, every news report, every TV show has data points sprinkled throughout.
- Government and official reports? Yup. Think of these as the “official” word on things.
And that’s just scratching the surface. There’s also:
- Financial breakdowns in financial statements and records. Like the pulse of the business world, these numbers tell tales.
- Historical data archives. The past, well, it’s got a lot of stories to share, and they’re all neatly stacked here.
- Academic gossip in encyclopedias and academic journals. All the latest theories, the debates, the breakthroughs? Right here.
- Not to forget the all-seeing, all-knowing web analytics and digital databases. Every click, every like, every share – they’re telling us something.
Advantages of Secondary Data
Swimming in this pool of pre-existing data? It’s got its perks.
For starters, convenience is the name of the game. A lot of it is just waiting, available at your fingertips. No need for fresh surveys, no waiting on feedback; it’s like fast food, but for research. And usually, it’s easier on the pockets. Dollar bills saved!
Then there’s the range. With secondary data, you can take a trip back in time or maybe even go global without leaving your chair. And for those who are like, “Research methods? Ain’t nobody got time for that!”, this is your jam. Dive deep without having to figure out the technical stuff.
Disadvantages of Secondary Data
Like everything, secondary data has its own shade of challenges. Primary data vs secondary data isn’t a superhero and sidekick situation. Both have their strengths, both have their quirks.
For one, secondary data might not always vibe with what you’re looking for.
Quality check? A must. You don’t want to base your conclusions on some iffy data that’s seen better days or, worse, has some serious bias issues. And if you’re looking for that unique angle, that fresh perspective, well, secondary data isn’t always your best bet.
Comparing Primary and Secondary Data
When you’re diving deep into the world of data, the clash of primary data vs secondary data can be like trying to pick a favorite ice cream flavor on a hot summer day.
Flavor One: The Freshness Factor
Imagine whipping up a meal.
Primary Data is like hand-picking every ingredient.
On the flip, Secondary Data? It’s more like using a pre-made sauce. Super convenient, and can taste absolutely delish, but there’s always a small part of you wondering about what’s really in it. Can you trust the label? How fresh is it?
Flavor Two: The Time & Money Hustle
Alright, so you’re planning a weekend adventure.
With Primary Data, think of it like planning a road trip from scratch. Choosing the stops, making the playlist, packing the snacks. It’s tailored to your vibe but dude, it can be a time sink. And your wallet? It can feel it too.
But Secondary Data? Think last-minute discounted group tour. It’s all there, planned out, and probably way cheaper. But…it’s not just your vibe. It’s everyone’s.
Deep Dive: The What-Ifs and Why-Nots
Every choice has its consequences, right?
When we talk Primary Data, there’s always that niggling thought – what if I missed out on something? Did I ask the right questions? Did my own biases sneak in there?
And for Secondary Data, there’s the whole dance of is this even legit? Was the data pure when it was first gathered? How many times has it been rehashed?
FAQ On Primary Data Vs Secondary Data
What’s the main difference between primary and secondary data?
Primary data is like getting firsthand gossip from your best friend about last weekend’s party. It’s raw, fresh, and straight from the source.
Secondary data, though? It’s like hearing the same story, but through the grapevine. It’s been passed around, and while it can still be juicy, it’s not as “untouched”.
Why would someone use primary data?
Ever had the urge to try a new restaurant just ’cause you wanna? That’s primary data for you. You want a taste of something specific, something tailored to your own needs. Primary data gives you that hands-on, direct info which can be perfect for answering specific questions.
And why choose secondary data?
Okay, think Netflix binge. You want something quick, without the hassle. Secondary data is already there, waiting, like those top 10 trending shows.
You don’t have to collect it yourself, which can save you a heap of time and money.
How reliable is primary data?
Imagine lending money to your childhood friend. You’ve known them forever, right? Primary data, when collected well, can be super reliable because you control the how and where.
But, just like friends, it’s not immune to occasional mistakes.
Is secondary data less trustworthy?
Ever played the telephone game? The more the story gets passed, the twistier it becomes. Secondary data can sometimes be like that.
It can be trustworthy, for sure, but since you’re not the one who gathered it, there’s a hint of unpredictability.
What are the costs like for primary data?
Primary data? It can be like planning a fancy date night at that high-end restaurant. Personalized, yes. Worth it, maybe.
But, there’s no denying it’s gonna cost you in time, effort, and actual money.
Can secondary data be outdated?
Totally. It’s like jamming to an old mixtape. It’s got classics, sure, but you might be missing out on the latest hits.
Secondary data might not always have the most recent info, so always check the “release date”.
What’s the best method to collect primary data?
Depends on what’s cooking! Sometimes a casual chat (interview) does the trick. Other times, you might want to pass around questionnaires at a fam reunion (surveys).
It’s all about what you’re curious about.
When is using secondary data a bad idea?
Think blind online shopping. Sometimes it’s a hit, sometimes a miss. Using secondary data without verifying its quality, source, or relevance to your needs might lead to those “wish I hadn’t” moments.
Can I mix both primary and secondary data in research?
Absolutely! It’s like blending your grandma’s secret recipe with a modern twist from YouTube.
Use primary data for that unique flavor and throw in secondary data to round it all out. Just remember, it’s all about balance.
Conclusion on Primary and Secondary Data
When wrapping our heads around the concept of primary data vs secondary data, it’s crucial to understand the inherent qualities and limitations of each.
Primary Data: This data is derived directly from the source. It’s untainted, untouched, and collected for the very first time. The accuracy is generally high, and it addresses specific research goals.
Secondary Data: This is data that has already been collected and processed by someone else. While it offers quick access and is often cost-effective, it may not always align perfectly with current research needs.
If you liked this article about primary data vs secondary data, you should check out this article about categorical data examples.
There are also similar articles discussing nominal vs ordinal data, discrete vs continuous data examples, descriptive statistics, and different types of data.
And let’s not forget about articles on how to present data visually, real-time data visualization, advantages of secondary data, and data visualization principles.