Introduced in wpDataTables version 7.3, the Index Column type provides automatic, fixed row numbering — shown as a sequential index (1, 2, 3, …).
This column cannot be edited manually and remains unaffected by sorting, filtering, editing, or pagination.
It’s especially useful when you need a consistent, visible row number for each entry — making it ideal for tables such as rankings, leaderboards, match results, ordered logs, or progress tracking.
Using the Index Column in an Example
To demonstrate how the Index Column works in practice, we’ll use a familiar example — a Premier League Standings Table.
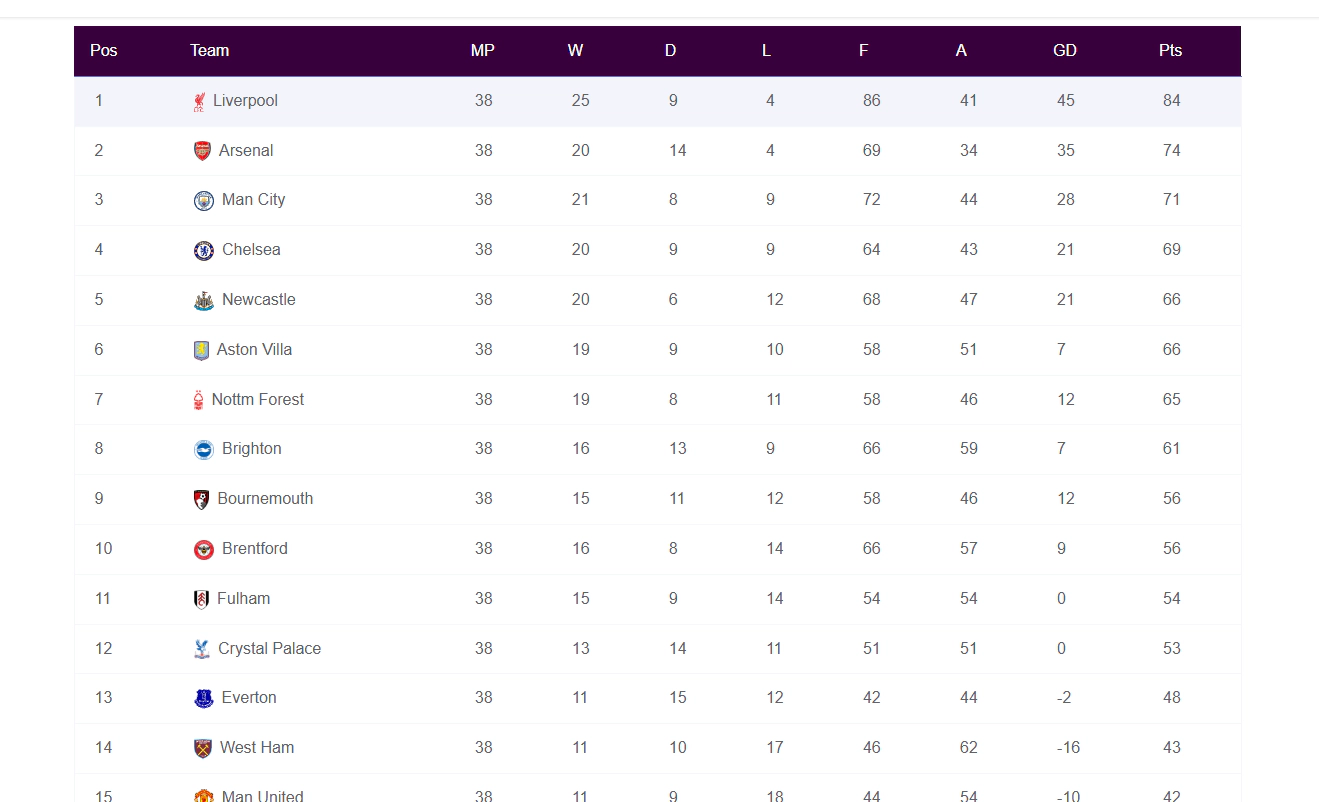
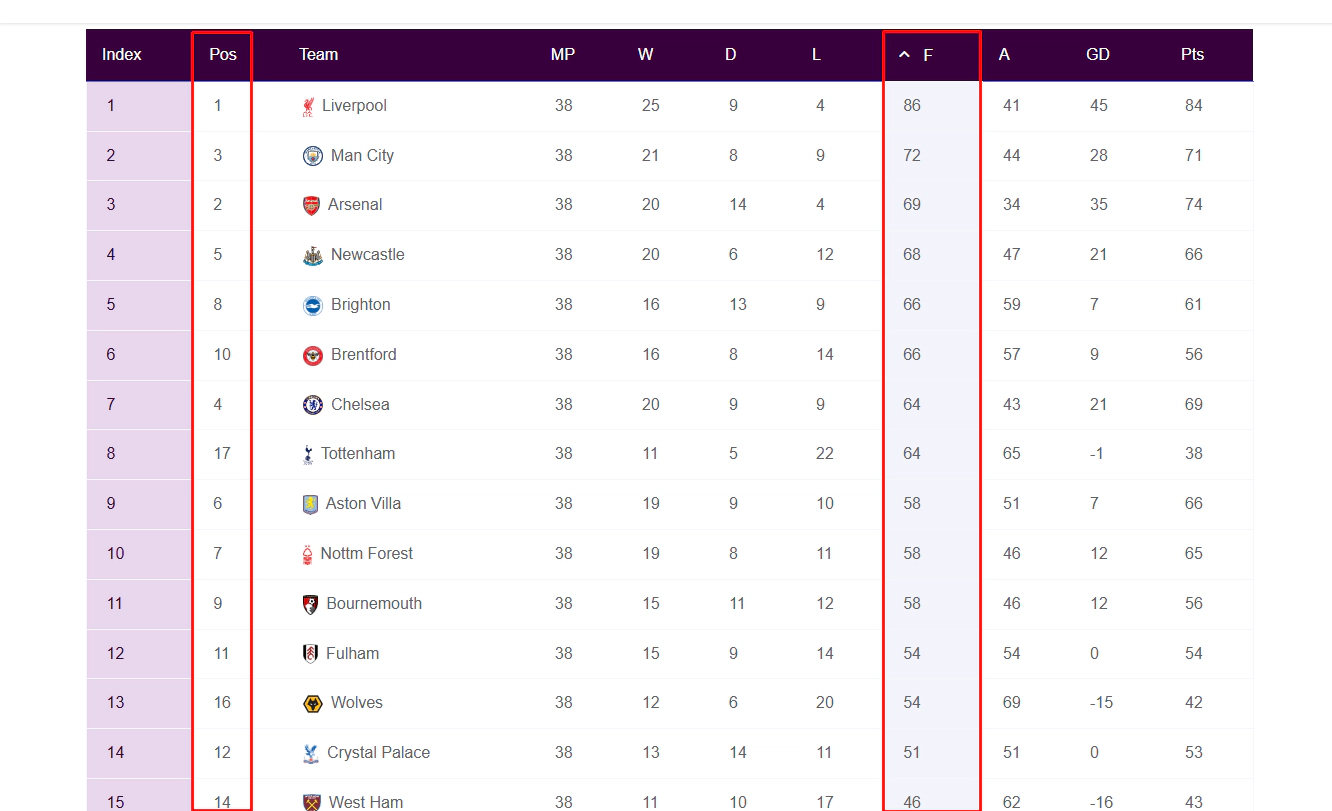
Here is a screenshot of how the table initially looks. Notice the first column labelled Position, which shows the current rank of each team. This is the default column the table is sorted by when it first loads.
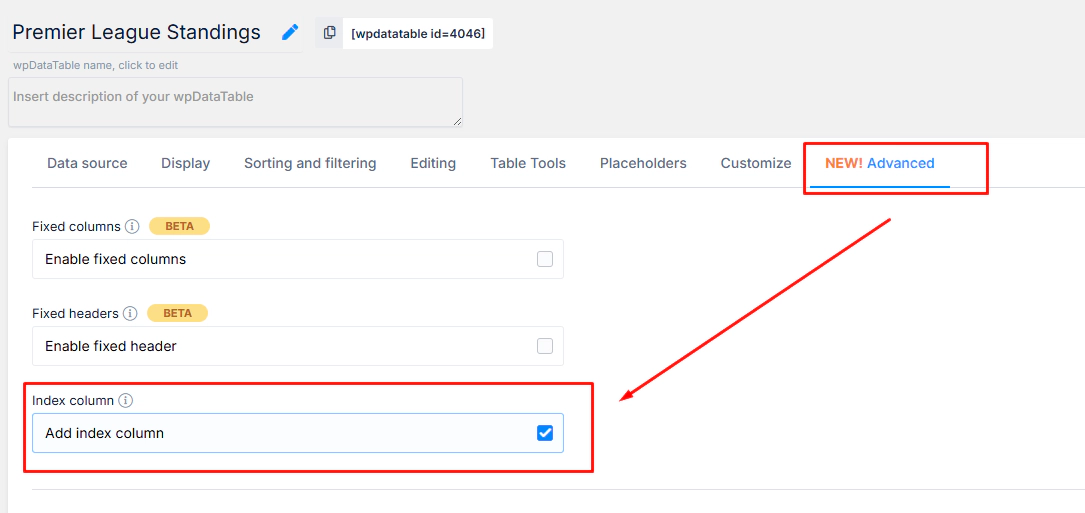
Now we’ll add the Index Column to this table. To do this, open the back-end table settings, navigate to the Advanced tab, and enable the “Index column” option.
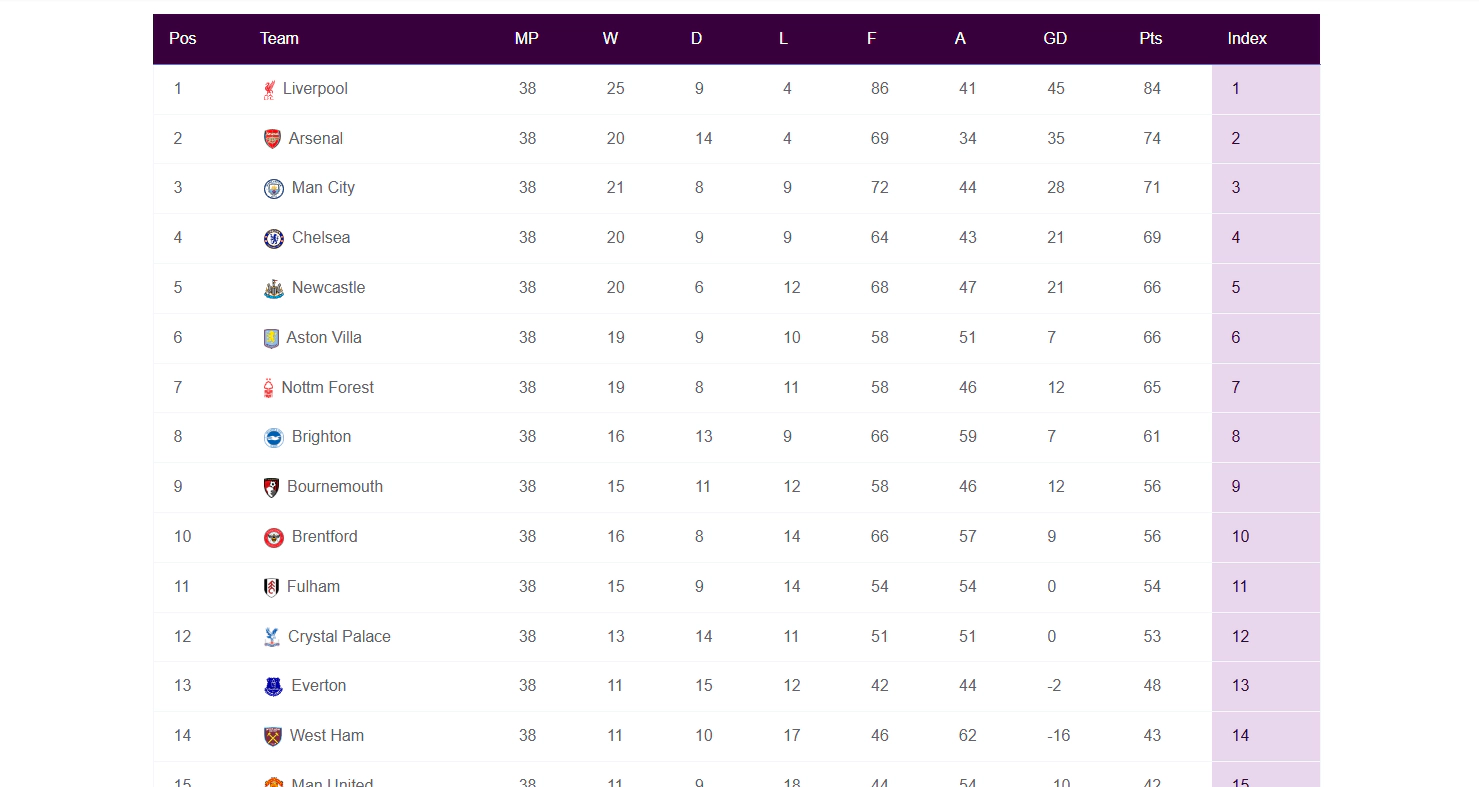
By default, the Index Column is added as the last column in the table.
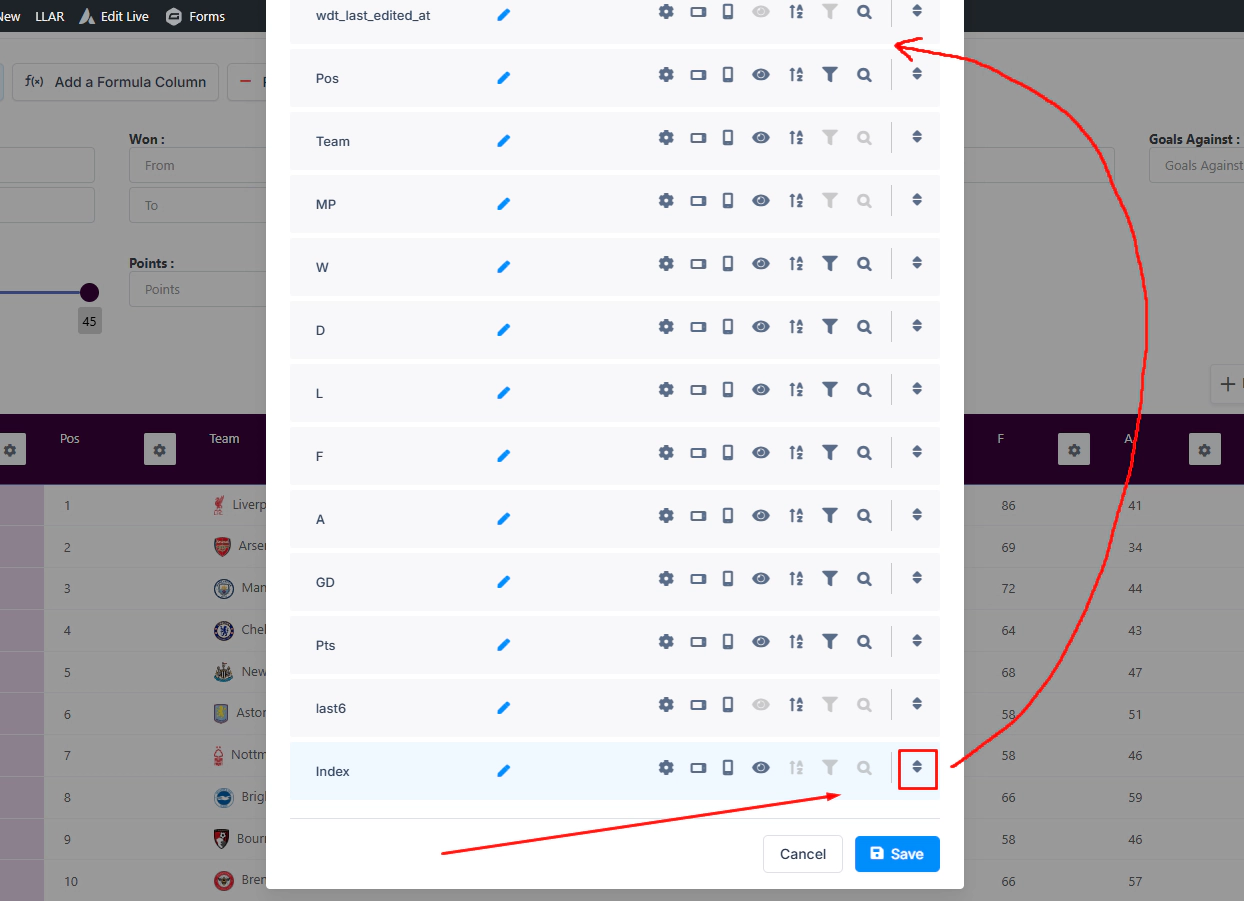
However, you can easily reorder its position from the Column list in the table’s back-end settings.
In this example, we’ll move it to the first column — placing it before the Position column.
Sorting the Table to Demonstrate the Index Column
To clearly show how the Index Column behaves independently from other data, we’ll now sort the table by the Goals For (F) column — which represents the number of goals each team has scored this season.
Teams with the highest-scoring offenses will move to the top, reshuffling the table order. However, the Index Column will continue to display sequential row numbers (1, 2, 3, …), based solely on the current visible row order — not the team’s actual rank in the league (Position column).
This helps illustrate how the Index Column always reflects the visual order of the table, no matter how the content is sorted.
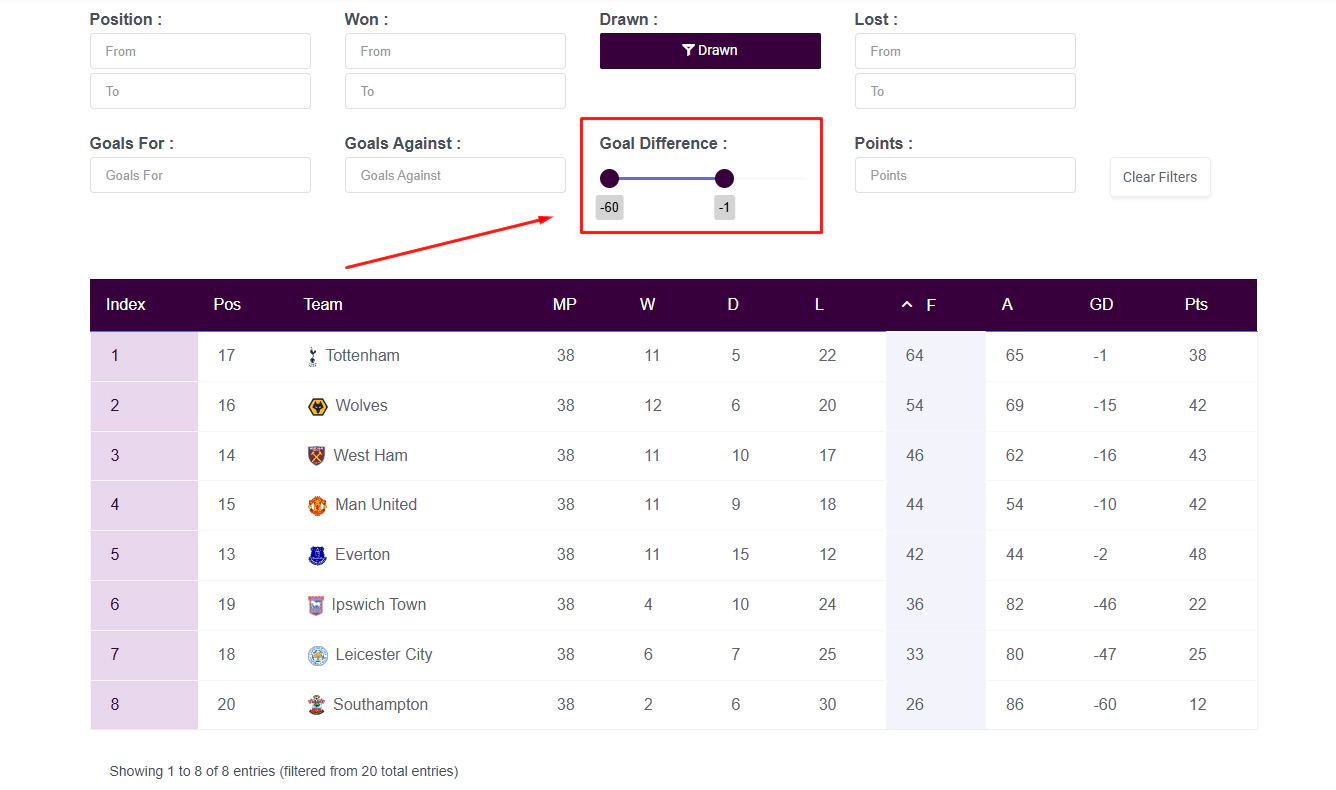
To further demonstrate how the Index Column works, we’ll now apply a filter to show only teams with a negative Goal Difference (i.e., teams that have conceded more goals than they’ve scored).
The table is still sorted by Goals For, but now only teams meeting this filter condition are displayed.
As always, the Index Column is recalculated to reflect the current visible order — starting from 1 and continuing sequentially through the filtered results.
This confirms that the Index Column is dynamic: it always shows the row number within the current view, regardless of how the table is sorted or filtered.
